Abstract
Introduction: Ph-like ALL is defined by a gene expression profile similar to Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL but lacking the BCR - ABL1 fusion. Ph-like ALL is comprised of diverse genomic alterations activating kinase and cytokine receptor signaling, including chimeric fusions involving ABL1 and related genes (ABL2, CSF1R, PDGFRB ; ABL-class fusions), genomic rearrangements leading to CRLF2 over-expression, JAK2 gene fusions, and truncating rearrangements of EPOR . We have published several large studies describing the clinical features, treatment outcome, and genomic alterations in Ph-like ALL that focused on patients with NCI high risk (HR) ALL (age ≥10 years or WBC ≥50,000) or those with SR ALL (age 1-9.99 years and WBC <50,000) and elevated minimal residual disease (MRD) at the end of induction (EOI; Reshmi, BLOOD 2017 and Roberts, NEJM 2014). The purpose of the current study was to assess the frequency of genomic lesions in Ph-like SR ALL patients lacking HR features.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 1023 unselected newly-diagnosed SR ALL patients enrolled on COG AALL0331 between 2006 and 2008, and compared characteristics of SR Ph-like cases to the HR patients described in our prior studies. All cases were screened using an 8-gene Taqman low-density array (LDA) PCR assay to identify the Ph-like GEP (Harvey, ASH 2013). Ph-like cases with elevated CRLF2 expression were tested for CRLF2 rearrangement (CRLF2 -R; P2RY8 - CRLF2 by Taqman PCR on the LDA card and IGH - CRLF2 by FISH). JAK mutations in CRLF2 -R cases were tested by Sanger sequencing. Ph-like cases without CRLF2 -R were tested for previously identified kinase fusions involving ABL1, ABL2, CSF1R, JAK2, NTRK3, and PDGFRB by RT-PCR. A subset of Ph-like cases without detected genomic alterations underwent RNA-sequencing using standard Illumina library preparation.
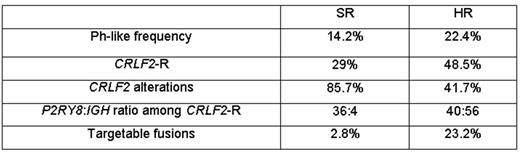
Results: A total of 205 patients had LDA value ≥0.5, with 145 (14.2%) remaining after exclusion of BCR-ABL1 and ETV6-RUNX1 . Of these 145, 85 were CRLF2high (57.9%) as defined by CRLF2 expression levels on the LDA card. Among these 85, 42 (50%) had CRLF2 -R, compared to 80% in HR patients. P2RY8 - CRLF2 was seen in 36 cases, IGH - CRLF2 in 4 and 2 had CRLF2 -R with an unknown partner; 14 (32.6%) of these had a concomitant JAK mutation. Of the 60 Ph-like CRLF2low cases, five had a targetable kinase fusion identified by RT-PCR or RNA sequencing: two ABL - class fusions (ZMIZ1 - ABL1, EBF1-PDGFRB); one PAX5-JAK2 fusion; one ETV6-JAK2 fusion; and one ETV6 - NTRK3 fusion. The 145 Ph-like cases had inferior 7-year event-free survival (EFS; 83.1±3.5% vs. 90.6 ±0.1%; P=0.005) and non-significantly inferior 7-year overall survival (OS; 93.5±2.3% vs. 95.5 ±0.8%; P=0.184) compared to 869 non Ph-like cases. Ph-like ALL cases were more likely to have end induction MRD ≥ 0.01% (24.3% vs. 17.9%; P=0.049), and positive MRD was predictive of outcome for Ph-like (7-year EFS: 73.2±8.3%, vs. 86.6 ±3.7%; P=0.079; 7-year OS: 88.2 ±5.9% vs. 95.9±2.1%; P=0.162) and non Ph-like patients (7-year EFS: 79.7 ±3.7% vs. 93.3 ±1.0%; P <0.0001; 7-year OS: 90.2% SE 2.7 vs. 97.4±0.9%; P <0.0001). In multivariate analyses, Ph-like and MRD status EOI were significant predictors of EFS (p=0.016; <0.0001 respectively), while only MRD had a significant impact on OS.
Conclusion: Ph-like ALL is less common in NCI SR than HR patients with significant differences in the frequency of various genomic alterations in Ph-like ALL cases based on NCI risk group. Our previous studies have shown that Ph-like ALL HR patients have a substantially increased risk of treatment failure and death as compared to non Ph-like HR patients (Mullighan, NEJM 2009 and Roberts, NEJM 2014). This cohort of SR Ph-like patients had a significantly inferior EFS and a trend to inferior OS, but the magnitude of effect was much smaller than that seen in HR Ph-like patients, with overall outcomes much better in SR as compared to HR Ph-like patients. These findings underscore the significant differences in Ph-like ALL frequency, genetic subtypes, and outcome based on age and initial WBC.
Borowitz: Beckman Coulter: Honoraria; Becton-Dickinson Biosciences: Research Funding; HTG Molecular: Honoraria. Zweidler-McKay: ImmunoGen: Employment. Mattano: HARP Pharma Consulting, LLC: Employment. Mullighan: Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy. Hunger: Amgen: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Novartis: Consultancy; Erytech Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.